“‘There is no such thing as an infant’, meaning, of course, that whenever one finds an infant one finds maternal care, and without maternal care there would be no infant.” (Winnicott, 1960, p. 585)
Abstract: In the first of a series of articles about early childhood development, the Michigan Association for Infant Mental Health’s (MI-AIMH) esteemed Michael Trout asked us to consider what is happening in the mind of expectant parents, particularly that of the mother. This article ponders the evolution of a neonate through the first year of life. Precisely because each baby is a being with unique biology, temperament, feelings, experiences, and ways of experiencing and learning, much is to be discovered and understood about them. The question of “what is going on in there?” is especially salient given that the baby’s wordless communication requires adult caregivers to intuit, infer, hypothesize and experiment. As we walk alongside parents who struggle to come to know their infant, we are required to have conceptual knowledge of how a newborn becomes a fully awakened infant. Beginning with the influence of parental perception, eloquently described by Trout, this chapter of our series will explore the development of attachment and how that influences relational expectations, communication, and social-emotional development. Each of these domains of development is impacted by factors other than attachment, but it is by now clear that babies grow in the context of relationship, and the quality of those relationships affects the physiological and psychological organization of the baby.
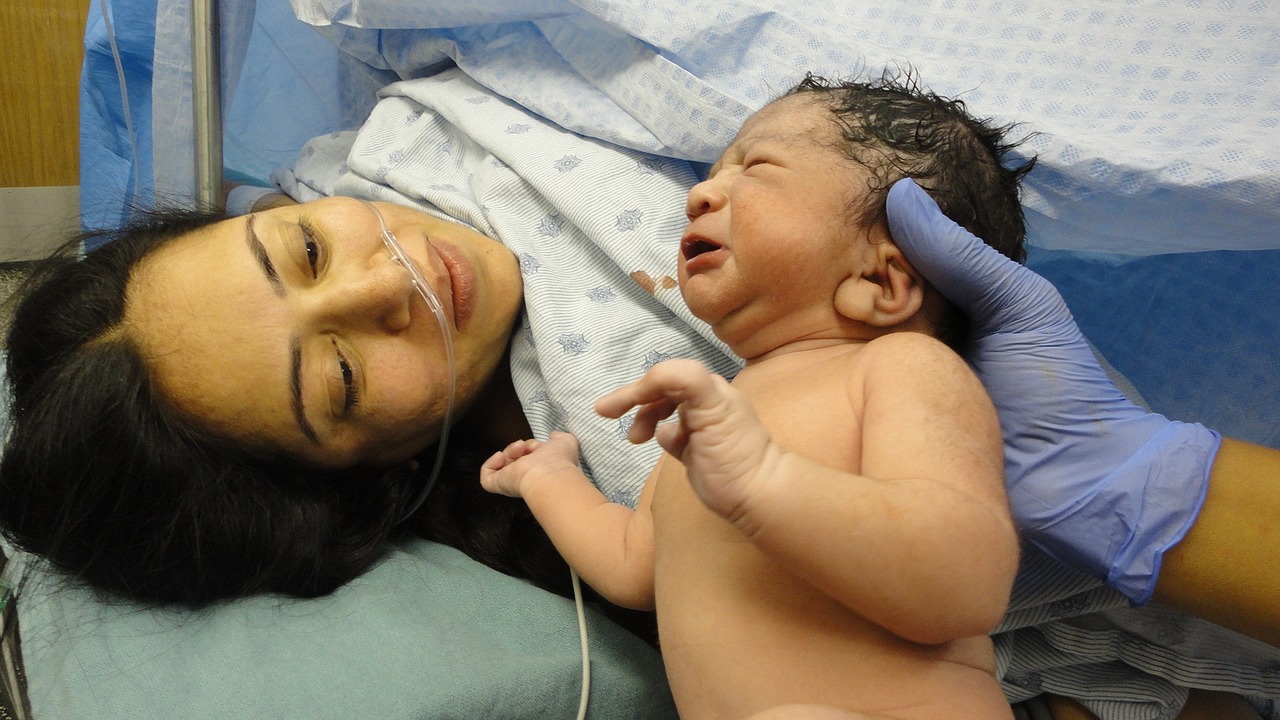
Isn’t She Lovely: The Birth
“What a glorious conclusion to the amazing developmental/psychological work of pregnancy: to be able, at the end, to say “Goodbye” in the service of saying “Hello.” (Trout, 2018)
Who is this tiny being the parent(s) are greeting? We are accustomed to hearing the search for clues: Who does he resemble? How does she cuddle in? Do they1 cry immediately or are they an “easy” baby? For the parents, the “real” newborn is meeting the “imagined” baby (Stern, 1999) and that encounter introduces the first threads of the unfolding relationship. The way the baby has been perceived throughout pregnancy is not inconsequential. Caregiver representations of their infant exert a powerful influence on the manner in which the baby’s signals and cues are experienced, comprehended and responded to (Rosenblum, Dayton, & Muzik, 2019; Dayton, Levendosky, Davidson, & Bogat, 2010;) and are indicated in the development of attachment (Vreeswijk, Maas, & van Bakel, 2012). If, as in Trout’s example on the developmental tasks of pregnancy (2018), the baby represents the mother’s ‘irrational, perhaps, but no less profound’ sense of failure to protect the baby from environmental toxins, then worries of normalcy or loss, and fears of inadequacy are likely to color the initial greeting — saying “hello” to this new being.
The transactional model (Sameroff, 2010; Sameroff & MacKenzie, 2003) elucidates the process by which parental perception is one pathway to infant outcomes. In a transactional way, first the “infants stimulate their parents, either through their appearance or behavior; second, the parents impose some meaning system on the input; and third, the parents then react with some form of caregiving (Sameroff & MacKenzie, 2003, p. 19). We can imagine a mother, already predisposed to conscious or unconscious worries about the health of her baby, selectively attending to behaviors that confirm her worry that she has irreparably harmed her baby. She may hear his cries as more intense or as signaling excessive fragility, and thus tend to him with a level of anxiety that is transmitted to him, intensifying his cries. Thus the cycle begins.
It does not have to play out this way, of course. There are a myriad of ways their interactions might unfold. A kindly nurse might normalize his cries, appease the mother’s worries and set the parent-infant relationship on a different course. A grandmother might note “Oh, he sounds just like you when you were a baby,” thus linking the past and the present in a way that affirms health and survival. For the IMH specialist, what is salient is that listening for the meaning of the baby to the parent is worthy of our careful attention as it offers a port of entry when there is a distortion or withdrawal from the baby. With an awareness that the baby may represent an array of past people and experiences, we can intervene to help the caregiver come to know the real baby.
Getting to Know You, Getting to Know All About You: The Early Weeks
In the first month of life, the neonate becomes increasingly physiologically adjusted to life outside the womb. They1 become familiar with the sights, sounds, smells, touch and movement that begin to shape their experience of the world. The physical and emotional nature of interaction with caregivers begins to develop the attachment relationship. Ainsworth, in her seminal work, spent hundreds of hours, first in Uganda, then in Baltimore, observing the developing relationship between babies and their mothers (Ainsworth, 1967; Ainsworth, Blehar, Waters & Wall, 1978). She identified four phases of the development of infant-mother2 attachment.
____________________
1They is a gender-neutral term for a person and will be occasionally used in this article. In most instances, though, for sake of clarity, the parent will be referred to as she and the baby as he or they.
2 Though Ainsworth and other early attachment studies focused on mothers, primarily because of the cultural context, “mothering” is non-gendered, and no inference is made that only females can be primary attachment figures.
In the early weeks of life, the “initial preattachment phase” (Ainsworth, et al., 1978, p. 23), the baby orients to any person who is in proximity, seeming not to differentiate the mother from other people. His inborn care-seeking behaviors include crying, “rooting, sucking, grasping and postural adjustments” (p. 23) that allow him to signal or maintain contact with another. Later research noted that neonates recognize the sound of their mother’s voice (DeCasper & Spence, 1986) and the smell of her breast milk (Marlier, Schaal, & Soussignan, 1998) so even though the baby may settle for a variety of caregivers, the presence of their mother is still sure to be a source of familiarity.
Once the newborn’s sensory systems begin to consolidate, they become increasingly capable of differentiating their primary caregiver from other people. Through smells, sounds and sight, they discern not only familiar from unfamiliar people, but between familiar people as well. It is in this phase, beginning between eight and 12 weeks and known as the “attachment-in-the-making phase,” that we notice the baby show differential smiles, settle for a few key caregivers more readily than others and more specifically orient and cue particular caregivers than others. A home visitor, asked to hold a baby for a few minutes while the mother attends to a toddler, might notice that they baby shifts his body in order to retain visual contact with the mother. In offering developmental guidance that supports the important emerging relationship with the primary caregiver, we have often been heard to say on a home visit, “Yes, yes, I know! You don’t know me and you want to be able to see your momma!”
Once an infant is capable of rolling, scooting, and crawling (i.e., approximately six through eight months), he is now capable of taking a more active role in seeking out proximity to his preferred caregiver. He may still occasionally prefer to signal through crying, smiling or reaching, but now, especially as he becomes increasing motorically competent, he is also able to scramble up on the parent, bury his head into a lap when anxious or alarmed, or crawl to a parent for a quick snuggle and emotional recharge. The capacity to locomote signals the onset of the phase of “clear-cut attachment.” The same capacity to seek out the caregiver also allows the child the ability to more actively explore the environment. It is the balance of the capacity to explore the environment and to return to a “safe haven” when alarmed, tired, hungry or ill that differentiates the quality of the attachment relationship. As Bowlby noted,
“All of us, from the cradle to the grave, are happiest when life is organised as a series of excursions, long or short, from the secure base provided by our attachment figures” (1988, p. 62).
Mounds and decades of research have described, studied and elaborated the styles of attachment relationships shaped in the first year of life. Through day-to-day interactive exchanges, babies begin to form schemas, or expectancies of their world, including mental maps of the self, the other and the self-in-interaction-with-the-other. Bowlby described these “internal working models” (1988, p. 165) as meaningful and reasonable ways of understanding the world in order to predict others’ behavior and to “plan” accordingly (realizing full well that this is a nonconscious process in the first year of life). In an era where much therapeutic treatment was constructed on the idea that babies were capable of generating and acting upon fantasies about their parents (Abram & Hinshelwood, 2018), Bowlby held fast to the notion that infants were responding to and developing ways of interacting with the actual environment. In other words,
if parents were accepting of the baby’s strong emotions or bids for interaction, the baby would begin to construct a sense of self as worthy of care and protection.
More current research has also confirmed his hypothesis that responsive caregiving during the first year of life plays a critical, though by no means sole, role in healthy development (Schore, 2005; Sroufe, Coffino & Carson, 2010 ).
Baby Mine: Patterns of Attachment
 Books and papers abound that describe the typical patterns of attachment. Briefly, attachment theory describes four basic styles of attachment: three “organized” styles (Ainsworth et al., 1978) and one “disorganized” style (Hesse & Main, 1999). In the organized patterns, the caregiver, during the first year of life, has responded in ways that are relatively consistent or predictable, allowing the baby to develop a mental map of what can be expected from their caregiver. Babies who by the end of the first year are coded as “secure” in standardized assessment procedures, most typically the Strange Situation Procedure (Ainsworth, et al., 1978; Sroufe, et al., 2010), have experienced reliable, predictable and sensitive responsivity from their caregivers (Bowlby, 1988). Their tender needs and their needs for exploration have been, on balance, accepted. They are confident in the knowledge that their parent is a source of safety, both psychic and physical, and thus they are free to explore their environment. These babies develop “positive expectations concerning relationships with others, beginning capacities for emotion regulation and object mastery skills because of how secure attachment promotes exploration” (Sroufe, et al. 2010, p. 46). For these babies and caregivers, relationships are a source of pleasure and joy. Home visitors may find themselves relieved to visit these families, noticing the sense of attunement and comfort in the parent-infant relationship. In the context of visiting families where poverty of resources, and sometimes poverty of hope, prevail, seeing babies who are secure is a welcome salve.
Books and papers abound that describe the typical patterns of attachment. Briefly, attachment theory describes four basic styles of attachment: three “organized” styles (Ainsworth et al., 1978) and one “disorganized” style (Hesse & Main, 1999). In the organized patterns, the caregiver, during the first year of life, has responded in ways that are relatively consistent or predictable, allowing the baby to develop a mental map of what can be expected from their caregiver. Babies who by the end of the first year are coded as “secure” in standardized assessment procedures, most typically the Strange Situation Procedure (Ainsworth, et al., 1978; Sroufe, et al., 2010), have experienced reliable, predictable and sensitive responsivity from their caregivers (Bowlby, 1988). Their tender needs and their needs for exploration have been, on balance, accepted. They are confident in the knowledge that their parent is a source of safety, both psychic and physical, and thus they are free to explore their environment. These babies develop “positive expectations concerning relationships with others, beginning capacities for emotion regulation and object mastery skills because of how secure attachment promotes exploration” (Sroufe, et al. 2010, p. 46). For these babies and caregivers, relationships are a source of pleasure and joy. Home visitors may find themselves relieved to visit these families, noticing the sense of attunement and comfort in the parent-infant relationship. In the context of visiting families where poverty of resources, and sometimes poverty of hope, prevail, seeing babies who are secure is a welcome salve.
Infants who develop insecure patterns of attachment lack confidence in the responsivity or availability of their caregivers. In one direction, babies who develop an avoidant attachment have experienced repeated rejection or rebuffing in times of heightened distress or fear. Their mothers, in home observations conducted by Ainsworth (Ainsworth, et al., 1978), were observed to experience irritability and anger in interaction with their baby far more often than mothers of secure babies. They showed a restricted range of affect and often did not enjoy physical contact with their baby. These babies, by the end of the first year of life, learn to minimize their displays of need by turning their attention away from caregivers, often toward toys or other inanimate objects. In addition to having to hide their need for comfort in order to avoid rejection, they also must mask their anger, lest it provoke more parental anger and rejection. As Bowlby described, “When in marked degree such an individual attempts to live his life without the support of others, he tries to become emotionally self-sufficient…” (1988, p. 124).
Infants who develop a resistant, aka ambivalent, attachment to their mothers are uncertain about their caregiver’s emotional availability. In the Minnesota longitudinal study (Sroufe, Egeland, Carlson, & Collins, 2005), mothers of future ambivalent children were the “least psychologically aware” of any mothers in the study. Ainsworth et al. (1978) found the mothers of ambivalent babies to be less rejecting of their babies than mothers of avoidant babies, but less sensitive to their babies’ signals than mothers of secure babies. While not averse to physical contact with their infants, they also were “inept” (p. 300) and awkward in their ministrations. These mothers appear to have difficulty consistently seeing and knowing “what is going on in there,” and the baby experiences a confusing array of unpredictable caregiving responses. By the end of the first year, ambivalent infants appear preoccupied with their mother’s whereabouts and, uncertain that their mother will be able to assist in times of discomfort, alarm or fear, are unable to use soothing, even when the mother offers it. They are less likely to explore their world and seem to say “It is hard to let go when I do not know if you will be there when I need you” (Ribaudo, 2016).
A fourth attachment pattern is labeled disorganized/disoriented. Identified later in attachment research by Main & Solomon (Main & Solomon, 1990), these babies show a collapse of their typical organized strategy (secure, avoidant or ambivalent) when faced with significant distress. Disorganized/disoriented infants are thought to have experienced frightened and/or frightening parental behavior (Lyons-Ruth, 2008) that is sporadic and unpredictable, or parental affective communication that is “disrupted and contradictory” (Lyons-Ruth, 2008, p. 675) such as mocking or teasing when the baby is distressed. When faced with distress, a disorganized baby tends to show contradictory behavior such as approaching a parent with averted head, or walking toward a parent as if to seek comfort but then walking past him or her. Parental withdrawal (directing the infant toward a toy when the baby seeks comfort) and disinterest in the baby (e.g., silent caregiving during daily routines) is a significant risk factor for the development of a disorganized attachment and later psychopathology (Lyons-Ruth et al., 2013). Disorganized attachment ranges from 13 percent in nonclinical samples to 90 percent in samples of maltreated children (Cicchetti, Rogosch, & Toth, 2006; Lyons-Ruth & Jacobvitz, 2008). Highlighting the intergenerational nature of patterns of relating, disorganized attachment is more prominent in dyads in which the parent has a history of unresolved loss or trauma in his or her own childhood (Hesse & Main, 1999). Duschinsky (2018) recently clarified the range of experience of fear or alarm in the presence of the caregiver, elaborating, for instance, that the caregiver may not be the direct source of harm but may be associated with fear due to being a cue for danger, as in the case of being exposed to parental interpersonal violence. In instances where the parent is a direct source of fear or threat to the baby, as in maltreatment, the home visitor is likely to experience moments of confusion, despair and helplessness as they watch dyads where the source of comfort (i.e., the parent) is at the same time the source of fear.
Talk to Me Baby: Communication
What is an infant trying to communicate through babbling sounds and coos? What does an infant’s extended eye contact with a caregiver reveal about their developing attachment? Infant communication starts at birth, and the ways in which infants and caregivers communicate in the first few months help build the attachment relationship.
Infants are born with the biological hard wiring for connection and begin to attend to their caregivers at birth. The quiet, alert state of a healthy newborn, who quiets to the voice and touch of the parent, is already engaging in and contributing to communication by virtue of this initial awake state. At two weeks, infants are able to follow their mothers’ gaze to external objects. By weeks seven and eight, infants exhibit social smiling in interactions, sustained eye contact, vocalizations and cooing, lip and tongue movements preparing their mouths for speech, and the ability to explore a communication partner’s face and start to gather and mirror back emotional cues (Lavelli & Fogel, 2013). As infants interact with their mothers in this second month, there is growth in what is sometimes referred to as “mother-infant coregulation processes”: Infants start to engage in short “turn-like dialogues” involving vocalizations and facial expressions like eyebrow raising (Lavelli & Fogel, 2013, p. 2266). These face-to-face interactions can be sustained longer by three to four months when infants develop the ability to engage in ongoing back-and-forth communicative patterns and to smile with full open mouths to display positive emotionality (Beebe & Steele, 2013). Between seven and 11 months, infants start to mimic sounds and behaviors of others, especially their mothers. They can respond to directing and pointing during one-on-one interactions, engage in ongoing babbling, and visually focus on objects or interactions with increased acuity (Dave, Mastergeorge, & Olswang, 2018, citing Albrecht & Miller, 2001).
Infants have an early ability to both pick up on and reciprocate physical and vocal cues from their mothers, and whether a mother is able to read and respond back to these signals is important for healthy language development and predictive of secure or insecure attachment. Mothers’ positive feedback to infants’ vocal sounds and expressions is largely responsible for developmentally appropriate communicative growth within secure attachments (Lavelli & Fogel, 2013). By two months, infants are less responsive to strangers’ vocalizations and smiles when they differ in affect from those of their mothers, suggesting that infants’ interactions with their mothers shape communication patterns with others (Lavelli & Fogel, 2013, citing Stern, 1974). Infants start to provide more vocal and expressive signals of their emotions at three months through smiles and coos, providing more attuned mothers with increased opportunities to mirror back their cues by smiling back or repeating their sounds. Infants whose mothers can provide this immediate vocal and facial feedback are shown to smile, gaze and coo at their mothers more than infants with less attuned mothers, who may disengage or become distressed when their communication is not reciprocated (Legerstee & Varghese, 2001). Thus, the home visitor or early interventionist is wise to carefully watch for the amount of reciprocity and vocalizations, especially in the fourth month, when we would expect to see increasing vocalizations.
Mothers’ abilities to follow their infants’ lead and engage in these positive back and forth communicative interactions are a key indicator of maternal sensitivity and the burgeoning stability or instability of the mother-infant attachment (Beebe, et al., 2010). Maternal ability to “stimulate” infants during periods of shared gaze with touch, vocalizations, and expressions and to hold back on stimulation when their babies looked away was positively correlated with secure attachment at 12 months (Beebe & Steele, 2013, p. 590). Likewise, a mother’s tendency to increase stimulation following “negative infant cues” such as breaking eye contact or showing signs of distress, and to withhold interaction when infants gaze and vocalize to them was positively correlated with insecure attachment at 12 months (Beebe & Steele, 2013, p. 590-591). Disorganized attachment at 12 months is, in part, predicted by maternal discordant affect, seen in mothers who display surprise or a smile when their baby shows distress (Beebe & Steele, 2013).
This reciprocity of vocal and facial expressions between mothers and infants extends beyond the ability to recognize and mirror back the infants’ communicative cues. During moments of mutual gaze, vocalizations, and play, infants and mothers derive a shared sense of each other’s emotions, mental states, and intent. Mothers with secure attachments shape their language and expectations based upon accurate understanding of infants’ abilities to comprehend their words and meaning (Dave, Mastergeorge, & Olswang, 2018). To illustrate this ability to provide responsive and appropriate communication, Dave, Mastergeorge and Olswang provide an example of a mother instructing her infant to “Give me the ball” at seven or 11 months, and the distinction in the appropriateness of this request based upon the infant’s developmental level.
By the same token, when mothers within insecure attachments are not attuned to their infants’ behaviors and vocalizations and unable to build reciprocity within the relationship, those patterns repeat themselves and limit prelinguistic development through 12 months and beyond. In insecure attachments, inconsistencies and rigidity in exchanges reverse the pattern of communication, with mothers, rather than infants, dictating vocalizations. Again, the infant’s sense of agency and verbal exploration is limited, often leading to the infant’s withdrawal (Lavelli & Fogel, 2013). Additional strain to communicative and linguistic growth can occur when mothers are depressed. Because caregiver communication consists in part of emotional affect and expression, social-emotional engagement is critical to infant-mother interactions. Even as early as the neonatal period, infants with depressed mothers tend to be less responsive to voices and faces (Dave, Mastergeorge, & Olswang, 2018; Field, Diego, & Hernandez-Reif, 2009; Lavelli & Fogel, 2013). Further, four-month-old infants of mothers with lowered responsiveness and emotional affect showed reduced self-contingency (Beebe et al., 2007; Lavelli & Fogel, 2013). Reciprocity between infants and mothers during the first year of life is an important contributor to prelinguistic development, attachment, and emotional development.
Do You Feel Like I Feel? Emotional Development
Throughout all the developments in cognitive systems and language, emotions hold the self together … Trevarthen, 2001, p. 114
How do babies experience emotions? What is present at birth and what is noticed later in infancy? How do parents observe and respond to their babies’ emotions? Does a cry represent a need for comfort or an attempt at manipulation? Is a smile perceived as an invitation to play or a smug taunt? Which emotions get attended to, elaborated, contained or rejected are influenced by parental perception and the budding attachment relationship.
Babies are born “wired” to experience and express emotions. Recent research has worked to elaborate what is seen on the outside, i.e. expressions, and what is experienced on the inside, i.e. which emotional displays correspond with which regions of the brain (Panksepp & Watt, 2011). It is beyond the scope of this article to review the scientific debate regarding what is universal vs. culture and experience in the development and display of emotions.
There is general consensus that newborns tend to display three discrete emotions: distress, positive/joy and interest (Rosenblum, Dayton & Muzik, 2019).
Each of these early primary emotions then evolve into more distinct and elaborated emotions such as anger, sadness, and more robust displays of joy, including laughter. By four months, infants can show anger at having a goal blocked (Izard, 2007) and perhaps even jealousy by six months (Rosenblum, Dayton & Muzik, 2019). It is important to note that emotions connected to self-awareness, such a guilt, shame or pride, are not observed until the second year of life. Awareness of the normative onset of emotions can assist the home visitor to attend to attributions made by the parent that are more likely to be a projection of the parent’s own disavowed emotion than an actual emotion experienced by the infant.
Rosenblum, Dayton and Muzik (2019) describe children who are well regulated in behavior and emotion as “better able to adapt to contextual and situational changes in the environment in a flexible and spontaneous manner (p. 103).” In infancy, the primary strategies available to babies include avoidance (gaze aversion, postural adjustments), displays of distress (crying), and self-comforting (touching, sucking) (Rosenblum, et al., 2019; Beebe, et al., 2010). Schore (2003) has noted that the caregiver’s capacity to modulate their own emotions, and thus more sensitively respond to their baby, influences the infant’s capacity to share pleasurable states and to find comfort and support that minimizes negative affects.
There are many pathways by which parental reactions to infant emotions begin to shape the emotional world of the baby, as well as their relationships. One important area we can observe and support is the parental capacity to accurately appraise and mirror back, in a slightly exaggerated fashion, their infant’s emotion (Gergely & Watson, 1996). This “marking” (Gergely & Watson, 1996), even of negative emotions, helps contain the infant’s emotions and assists in the process of an infant beginning to know that their internal state can be “felt” by others. For example, the parent who responds with a “woe face” (Beebe, et al., 2010) to a baby’s distress, saying “Aww, you don’t like that; that made you sad” is communicating to the infant that their internal experience can be shared and comprehended by another, that the internal feeling “looks” like what they see on their parent’s face (i.e., they see a “mirror” of what they are feeling), and that there are words that accompany the experience. This process of marking and containing, done repeatedly in the first years of life, lays the foundation for a child to know their own internal state, find words for them, and thus be able to share them with others, as well as empathize with the internal states of others. In other words,
a baby whose emotional world has been, for the most part, accurately interpreted and responded to through parental affect, tone of voice and words, is well on their way to being the toddler in the child care center who offers his binkie to a distressed peer or pats a crying baby.
They are also well on their way to gleefully shouting “Me did it!” and sharing their delight at success with the caregiver, having full confidence in the admiration of the caring adult. Having been seen, known, understood, and accepted, they are on their way to doing so for others.
The Ants Go Marching: The Journey into Toddlerhood
By the end of the first year, the neonate has evolved into a fully-fledged human, capable of expressing strong emotions such as love, sadness, fear, jealousy, and anger, and full of their own ideas, thoughts, intentions, wishes and desires. The scientist in the crib (Gopnick, Meltzoff & Kuhl, 1999) has become the scientist in the high chair. Returning to our example, what has become of the neonate whose mother feared she has irreparably harmed him in utero? Has his robustness registered and allowed her to feel reassured? Has her partner or a family member buffered or appeased her worry or have comments only heightened her anxiety? Has she found the words to share her worry and begun to see him in a different light? Has she developed confidence in her own capacity to help him with any struggles, real or perceived, despite her worries about the toxic exposure? Her resolution to the prenatal anxiety will have shaped his experiences in the first year. What nascent sense of self will accompany him into the journey into toddlerhood?
References
Abram, J., & Hinshelwood, R. (2018). The Clinical Paradigms of Melanie Klein and Donald Winnicott. London: Routledge.
Ainsworth, M.D.S. (1967). Infancy in Uganda: Infant Care and the Growth of Love. Baltimore, MD: The Johns Hopkins Press.
Ainsworth, M.D.S., Blehar, M.C., Waters, E., Wall, S. (1978). Patterns of Attachment: A Psychological Study of the Strange Situation. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Beebe, B., Jaffe, J., Markese, S., Buck, K., Chen, H., Cohen, P.,…Feldstein, S. (2010). The origins of 12-month attachment: A microanalysis of 4-month mother–infant interaction. Attachment & Human Development, 12, 3-141.
Beebe, B., Jaffe, J., Buck, K., Chen, H., Cohen, P. Blatt, S.,…Andrews, H. (2007). Six-week postpartum maternal self-criticism and dependency and 4-Month mother–infant self- and interactive contingencies. Developmental Psychology, 43: 1360–1376 .
Beebe, B., & Steele, M. (2013). How does microanalysis of mother–infant communication inform maternal sensitivity and infant attachment? Attachment & Human Development, 15, 583–602.
Bowlby, J. (1988). A Secure Base: Parent-Child Attachment and Healthy Human Development. New York, NY: Basic Books.
Cicchetti, D., Rogosch, F., & Toth, S. (2006). Fostering secure attachment in infants in maltreating families through preventative interventions. Development and Psychopathology, 18, 623-649.
Dave, S., Mastergeorge, A. M., & Olswang, L. B. (2018). Motherese, affect, and vocabulary development: dyadic communicative interactions in infants and toddlers. Journal of Child Language, 45, 917–938.
Dayton, C.J., Levendosky, A.A., Davidson, W.S., & Bogat, G.A. (2010). The child as held in the mind of the mother: The influence of prenatal maternal representations on parenting behaviors. Infant Mental Health Journal, 31, 220–241.
DeCasper, A.J., & Spence M.J. (1986). Prenatal maternal speech influences newborns’ perception of speech sounds. Infant Behaviour and Development, 9: 133–150.
Duschinsky, R. (2018). Disorganization, Fear and Attachment: Working Towards Clarification.
Infant Mental Health Journal, 39, 17–29.
Field, T., Diego, M., Hernandez-Reif, M. (2009). Infants of depressed mothers are less responsive to faces and voices: A review. Infant Behavior and Development, 32: 239–244
Gergely, G & Watson, J. S., (1996). The social biofeedback model of parental affect-mirroring. The International Journal of Psychoanalysis, 76, 1181-1212.
Gopnik, A., Meltzoff, A. N., & Kuhl, P. K. (1999). The scientist in the crib: Minds, brains, and how children learn. New York: William Morrow & Co.
Hesse, E., & Main, M. (1999). Second‐generation effects of unresolved trauma in nonmaltreating parents: Dissociated, frightened, and threatening parental behavior. Psychoanalytic Inquiry, 19, 481–540.
Izard, C. E., (2007). Basic emotions, natural kinds, emotion schemas, and a new paradigm. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 2, pp. 260-280.
Izard, C. E. (2009). Emotion theory and research: Highlights, unanswered questions, and emerging issues. Annual Review of Psychology, 60, 1–25.
Lavelli, M., & Fogel, A. (2013). Interdyad differences in early mother–infant face-to-face communication: Real-time dynamics and developmental pathways. Developmental Psychology, 49, 2257–2271.
Legerstee, M., & Varghese, J. (2001). The Role of Maternal Affect Mirroring on Social Expectancies in Three-Month-Old Infants. Child Development, 72, 1301–1313.
Lyons-Ruth, K., & Jacobvitz, D. (2008). Attachment disorganization: Genetic factors, parenting contexts, and developmental transformation from infancy to adulthood. In J. Cassidy & P. R. Shaver (Eds.), Handbook of attachment: Theory, research, and clinical applications (pp. 666-697). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Lyons-Ruth, K., Bureau, J.F., Easterbrooks, M.A., Obsuth, I., Hennighausen, K., & Vulliez-Coady, L. (2013). Parsing the construct of maternal insensitivity: Distinct longitudinal pathways associated with early maternal withdrawal. Attachment & Human Development, 15, 562-582.
Main, M., & Solomon, J. (1990). Procedures for identifying infants as disorganized/disoriented during the Ainsworth Strange Situation. In M.T. Greenberg, D. Cicchetti, & E.M. Cummings (Eds.), The John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur Foundation series on mental health and development. Attachment in the preschool years: Theory, research, and intervention (pp. 121-160). Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Marlier L., Schaal B., Soussignan R. (1998). Neonatal responsiveness to the odor of amniotic and lacteal fluids: A test of perinatal chemosensory continuity. Child Development 69: 611–23.
Panksepp, J., & Watt, D. (2011). What is basic about basic emotions? Lasting lessons from affective neuroscience. Emotion Review, 3, 387–396.
Ribaudo, J. (2016). Restoring safety: An attachment-based approach to clinical work with a traumatized toddler. Infant Mental Health Journal, 37, 80–92.
Rosenblum, K.L., Dayton, C.J., & Muzik, M. (2019). Infant social and emotional development: Emerging competence in a relational context. In C.H. Zeanah (Ed.), Handbook of Infant Mental Health (4th ed., pp. 95-119). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Sameroff, A.J. (2010). A Unified Theory of Development: A Dialectic Integration of Nature and Nurture. Child Development, 81, pp. 6-22.
Sameroff, A.J. & MacKenzie, M. J. (2003). A quarter-century of the transactional model: How have things changed? Zero to Three, 24, 14-22.
Schore, A.N. (2003). Affect dysregulation and disorders of the self. New York, NY: Norton.
Schore, A. N. (2005). Attachment, affect regulation, and the developing right brain: Linking developmental neuroscience to pediatrics. Pediatrics in Review, 26, 204-217.
Sroufe, L.A., Egeland, B., Carlson, E.A., & Collins, W. A., (2005). The development of the person: The Minnesota study of risk and adaptation from birth to adulthood. New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Sroufe, L. A., Coffino, B., Carlson, E.A. (2010). Conceptualizing the role of early experience: Lessons from the Minnesota longitudinal study. Developmental Review, 30, 36-51.
Stern, N. B. (1999). Motherhood: The emotional awakening. Journal of Pediatric Health Care, 13, 8-12.
Trevarthen, C. (2001). Intrinsic motives for companionship in understanding: Their origin, development, and significance for infant mental health. Infant Mental Health Journal, 22, 95–131.
Trout, M. (2018). What is going on in there? Infant Crier, Fall 2018. Michigan Association for Infant Mental Health
Vreeswijk, C.M.J.M., Maas, A.J.B.M., & Van Bakel, H.J.A. (2012). Parental representations: A systematic review of the Working Model of the Child Interview. Infant Mental Health Journal, 33, 314– 328.
Winnicott, D.W. (1960). The theory of the parent-infant relationship. International Journal of Psychoanalysis, 41, 585-595.